Theobroma cacao, the Fruit of Gods
The origin of this tropical understory tree in the family of the Sterculiaceae are the Amazon Headwaters from where it moved to Central America. Cocoa cultivation began by Mayan tribes in Central America, ca. 1500 BC. Mayas and Aztec attributed divine origin to cocoa tree (brought by god Quetzacoatl). The precious cocoa beans were used as a currency. The sacred beverage called "chocolatl" was consumed from golden cups.
 |
 |
 |
Cocoa was exported to Europe in 1585 but the first chocolate bar was not made until 1848. The purine alkaloids theobromine and caffeine are responsible for the stimulant effect of cocoa and chocolate and contribute to bitter cocoa flavor. |
The tree grows between ±15 ° latitude, requires 18-32 °C and 1500-2000 mm rain with high humidity. The tree grows 12-15 meter tall (in plantations ~ 7m). Seedlings form a jorquette (shown) with 5 plagiotropic branches. |
After 2-3 years the tree produces many cauliflorous flowers and fruits develop after about 5 years. |
 |
 |
 |
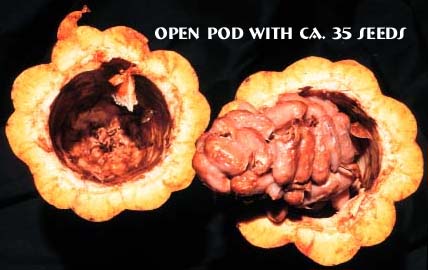
The fruits grow for 150-180 days, contain 30-40 seeds surrounded with mucilaginous pulp, and produce 10-35 cm long pods with recalcitrant seeds (no germination after dessication). A good tree produces up to 40 pods/year |
The plant is pollinated by midges (Forcipomyia sp). 60% of the flowers never get pollinated, & abscise within 48 hours. Only about 5% of pollinated flowers receive enough pollen to initiate fruit development. |
The flowers are small but exquisetly complex and delicate. Flower have characteristic, long pedicels and their cup-shaped petals form a hood over the fertile stamens. Five sepals and sterile staminodes surround the pistil. |
Diseases of Cocoa:Up to 30% of World's production is lost mostly through
fungal deseases such as: |
 |
More info on self-incompatibility!The self-incompatibility of Theobroma cacao
is an important issue. The fruits abscise several weeks after pollination.
Self compatibility is rare but important for breeding. |