Solid Phase Gene Extraction
Although much information can be gained from direct measurements of physical parameters, the ultimate control in living systems depends on information processing.In addition to using artificial statoliths to investigate force- and relocation effects on gravitropism (in Chara) it is important to investigate gene expression as a response to physiological stimulation. We have developed a novel mRNA extraction procedure that relies on needles = solid phase) that are poly-dT coated. This procedure can extract quantitative information of many gene in a particular region of tissue and even cells, not just the total mRNA that is typically obtained by processing large tissue. The fast and reliable in situ sampling shows remarkable consistency in the PCR-amplified mRNA signature. We have observed diurnal and spatial differences in single Chara internodal cells.
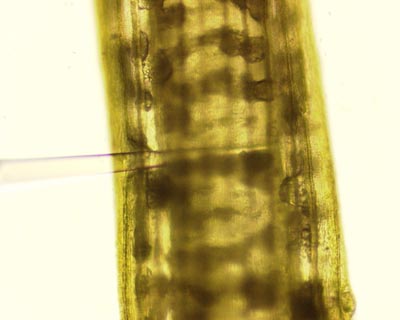 Chara internodal cell impaled with a SPGE probe. We sampled single cell up to 16 times without obvious damage. |
 A Chara internodal cell was probed at two different positions followed by RT-PCR. The samples (groups of 4 lanes, left to right) were taken from the periphery of the cell. The first and third group were taken one h after illumination, samples two and four were taken one h after dark. The similarity between the samples indicates a diurnal pattern. SPGE is capable of analyzing spatial and temporal patterns of gene expression in single cells. SPGE is the only method that can sample living systems repeatedly. |
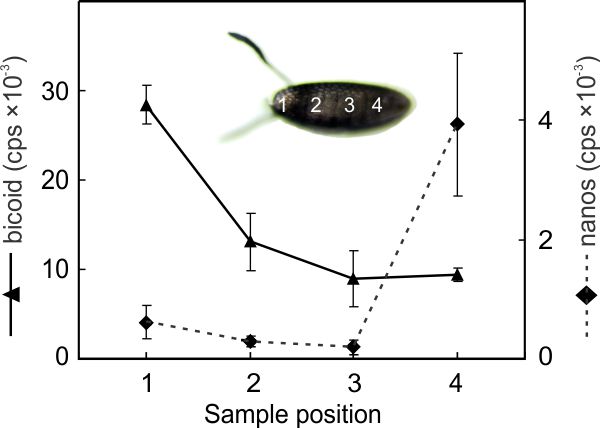 This example shows the probing of a Drosophila egg at four positions and subsequent quantification of bicoid and nanos genes. These genes are secreted by nurse cell and the gradients chaneg rapidly. Eggs survived the probing and developed into normal flies. |
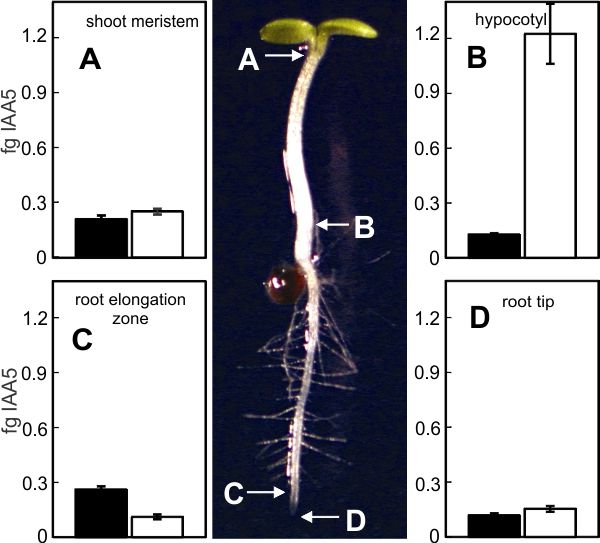 The sampling of an Arabidopsis seedling showed dramatic differences in the expression of IAA5 before (black bars) and after (white bars) auxin application. |
Because of greater mechanical stability we now use stainless steel needles and apply the technique as illustrated below: |
|
 A Brassica seedling was sampled at five different positions. |
  Transcription of highly expressed (Actin7 and ubiquitin, left) and low expressed genes(tubulin1 and glucokinase, right) genes in a seedling root at five different positions shows remarkable differences of gene expression. |